Consultation available in Japanese | Chinese | English
Incorporate in Japan Gerbera Support
Gerbera Partners' team of specialists in Accounting & Tax, Social Insurance and Labor and Judicial
Scriveners will treat your business with the utmost care where every order is important.
【Tokyo Office】7F Shuwa Sanchome Bldg, 3-23-6 Toranomon, Minato-ku, Tokyo
【Osaka Office】3F Honmachi Heisei Bldg, 1-2-12 Itachibori, Nishi-ku, Osaka
【Fukuoka Office】4F More Grand Bldg, 1-5-8 East Hakata Station, Hakata-ku, Fukuoka
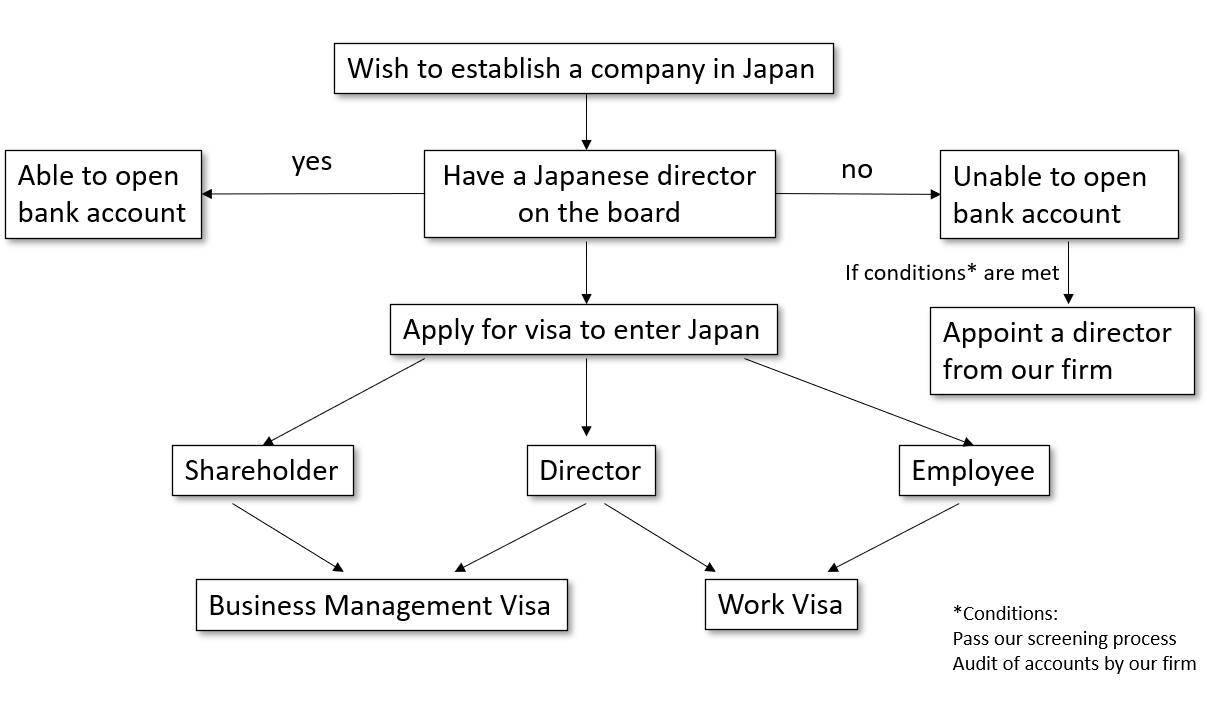
Incorporating in Japan
Incorporation Options
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Inexpensive to establish.
Its social perception is lower than
that of a joint-stock company.
Certification of articles of
incorporation is not required and
investors have no legally stipulated
term of office. A representative can
call themselves the president or
CEO, but he or she cannot call them
selves the “representative director”.
If the investor (shareholder) is not a
managing partners, there is no need
to change the registration.
Joint-stock Company
It’s possible to raise funds using
stocks. The company can be publicly
listed. Its more socially credible than
an LLC. There is an obligation to
report your financial statements.
(Since there is no penalty, the only
companies that report it are publicly
isted companies and companies
that are going through restructuring)
General Incorporated
Association
A corporation for the purposes of
public interest, unlike an LLC or a
joint-stock company. Dividends
cannot be paid; registration is
required every two years. There is
an obligation to report your financial
statements. Becoming a public
interest incorporated association
provides tax advantages. (but the
are a lot of hurdles to get by)
Comparison of Types of Business Operation
|
| LLC | Joint-stock Company | General Incorporated Association | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Business objectives | Unrestricted | ||
| Responsibility of | Limited Liability | |||
|
| Body of Law | Corporate Law | General Incorporated Association Law | |
| Purpose | Profit (Pay dividens) | Non-profit (No payment of dividends) | ||
| Organization type | Small scale companies | Small to large scale companies | ||
| Ownership and management seperation | No | Yes | ||
| Reorganization | Possible ( between LLC and Joing-stock Company | Not possible | ||
| Traits | Moderate name recognition and creditiblity | Good credibility | Possibility of becoming a ublic interest incorporated association | |
| LLC | Joint-stock Company | General Incorporated Association | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Profit distribution | Possible (no need to follow the equity percentage) | Possible (allocated according to equity participation ratio) | Not possible⇒Employee compenstaion | |
| Capital | 1 Yen or more | No capital⇒Fund system | ||
| New shareholders | Investment required | No investment required | ||
| Decision-making body for important matters | General meeting of members | General meeting of shareholder | General meeting of members | |
| Second term registration | Unnecessary | Necessary | ||
| Term | No limit | 2 to 10 years (directors) | 2 years | |
| Membership registration | Necessary (managing parterns, representative partners) | Unnecessary | ||
| Obligation to give public notice of accounts | No | Yes | ||
| LLC | Joint-stock Company | General Incorporated Association | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of members required | 1 | 3 | ||
| What to prepare | Company seal Deposit of capital Obtaining company seal impression etc. | Company seal Obtaining company seal impression etc. | ||
| Declaration of actual company leader | Unnecessary | Necessary | ||
| Certification of articles of incorporation | Unnecessary | Necessary ( about 50,000 JPY) | ||
| Stamp dity on articles of incorporation | 40,000 JPY (no cost with eletorinic articles of incorporation) | No | ||
| Registration and license tax | 0.7% of capital (minimum 60,000 JPY) | 0.7% of capital (minimum 150,000 JPY) | 60,000 JPY | |
| Gerbera Service | <In Japanese>80,000~100,000 JPY、<In other languages*>150,000~200,000 JPY *English, Chinese, Vietnamese | |||
Process of Establishing a Company, Visa Acquisition
and Entry to Japan
Entry to Japan on a short-term visa
Research and preparation for incorporation
Registration of incorporation and establishment
Application for Certificate of Eligibility for Residence to the
Immigration Bureau(after company registration)
Obtain Certificate of Eligibility for Residence
Visa application with Certificate of Eligibility at Japanese
diplomatic mission abroad
Acquisition of Visa at Japanese diplomatic mission abroad
Entry into Japan, seal of landing verification, issuance of residence card
Process of Incorporation
Joint-Stock Company
Determination of profile of joint-stock company to
be established and establishment of office
Preparation of LLC’s articles of incorporation
Acquisition of registratioin certificates, etc. for
parent company, affidavit regarding profile of parent
company and affidavits regarding signatures of
representatives of parent company
Notarization of joint-stock company’s articles of
incorporation by Japanese notary
Remittance of joint-stock company capital to
account of incorporator, representative director,
or director at incorporation
Appointment of directors, representative
directors and corporate auditors
directors and corporate auditors
Examination by directors and auditors
of legality of establishment
procedures and incorporation date
of legality of establishment
procedures and incorporation date
Application at the Legal Affairs Bureau for registration of joint-stock company establishment (joint-stock company establishment date); registration of company seal at the Legal Affairs Bureau
Acquisition of certificate on registered information and company seal impression certificate
Opening a bank account under company name
Notification of incorporation to the tax office and
local government
Notification of stock acquisition to the Bank of
Japan (notification prior to company establishment
may be required in certain sectors)
LLC
Determining the profile of LLC to be established
and establishment of the office
and establishment of the office
Preparation of articles of incorporation
Acquisition of registration certificates for companies that will become equity participants, affidavits
regarding signatures of representatives of parent
company, etc.
Notarization of LLC’s articles of incorporation by
Japanese notary
Payment by members of investment
Application at the Legal Affairs Bureau for
registration of establishment of LLC (LLC
establishment date), registration of company
seal at the Legal Affairs Bureau
Acquisition of certificate of registered information
and company seal impression certificate
Opening a bank account under company name
Notification if incorporation to the tax office and
local government
Notification of stock acquisition to the Bank of
Japan ( Notification prior to company establishment
may be required in certain sectors)
Necessary Documents for Incorporation
Joint-Stock Company
- Document(s) certifying that the foreign company has
decided to establish a subsidiary company (record of
proceedings) - Foreign company's articles of incorporation, establishment
certificate, registration certificate and other official
documents - Affidavit of the profile of the foreign company
- Document(s) certifying the authenticity of the signature of
the foreign company's representative - Article of incorporation of the Japanese corporation
- Certificate of remittance of the Japanese joint-stock
company capital - Record of proceedings on appointment of directors and
other officers of the Japanese corporation - Signature and seal certificate of the Japanese corporation’s
representative director - Signature and seal certificate of the Japanese corporation’s
directors - Report of company establishment procedures, etc.
LLC
- Document(s) certifying that the foreign company has
decided to establish a subsidiary company (record of
proceedings) - Foreign company's articles of incorporation, establishment
certificate, registration certificate and other official
documents - Affidavit of the profile of the foreign company
- Appointment or acceptance letter of executive officers
(representative member in the case of a corporation) - Signature certificate of the representative of the foreign
company - Article of incorporation of the Japanese LLC
- Certificate of remittance of payment by members of
investment stipulated - Seal certificates of representative members and executives
of the Japanese LLC
Proof of Investors

When establishing a company in
Japan, the investors of the
company (or its representatives if
the investors are companies) must
submit documents to the Legal
Affairs Bureau to prove that it is a lawful and legitimate
individual or entity.
Proof of Directors

When establishing a company in
Japan, the directors of the
company (and the auditors, if any)
must submit documents to the
Legal Affairs Bureau to prove that
he/she is a lawful and legitimate individual.
General Rule
If the investor has an address in Japan, submit the seal
registration certificate. It can be acquired at the municipal
office.
Special Case
In the case the investor is a company
If the company and its representatives do not have an
address in Japan, an affidavit (statement for China) should
be prepared locally and certified by a notary public. It will
be then translated to Japanese. The affidavit must contain
name, address and date of birth.
If the investor is a corporation, prepare an affidavit from
the representative of the corporation. Some affidavits may
or may not have a template at the notary public. We can
provide an English version if required. Affidavit may
require a letterhead.
A notary public is a notary office that has jurisdiction over
its area, for example a notary office in China has
jurisdiction over territories in China and a notary office in
Hong Kong has jurisdiction only in Hong Kong.
General Rule
If the investor has an address in Japan, submit the seal
registration certificate. It can be acquired at the municipal
office.
Special Case
If the individual does not have an address in Japan
( haven’t registered their address), ask a notary public to
notarize their signature ( or seal certificate) in the country
of your nationality. It will then be translated to Japanese.
Proof of signature must include the individuals name,
address and date of birth.
Required Notifications after Registration
National tax authorities
- Notification of incorporation in case of a subsidiary corporation
File within 2 months from date of incorporation - Notification of acquisition of status of foreign ordinary corporation in case of a branch
File within 2 months from date of acquisition of status of foreign ordinary corporation - Application for approval of filing a blue form tax returns
Public employment security authorities
-
Notification of coverage of establishment by employment insurance
(including notification of acquisition of insured status) -
This must be filed within 10 days of first hiring workers
Labor standard inspections authorities
- Labor standards enforcement report
- Labor insurance: notification of establishment of labor insurance relationship and declaration of
estimated insurance contribution - Agreement on overtime and holiday work
- Rules of the employment
Pension authorities
*“Employees” here also includes representative of corporations, such as representative directors
- Notification of first-time coverage by health/employees’ pension insurance
File within 5 days of first hiring employees at a corporation or other establishment covered by
social insurance - Notification of acquisition of insured status under health/employees’ pension insurance
File within 5 days of hiring employees - Notification of addition/removal of dependents of insured employee
Files within 5 days if a person (employee) covered by health insurance had dependents - Notification of acquisition of type 3 insured status under the National Pension
File within 5 days if a spouse of an insured person (employee) is dependent
Prefectural and municipal tax authorities
- Notification of incorporation or establishment of branch
Must be filed with each of the prefectural and municipal authorities to
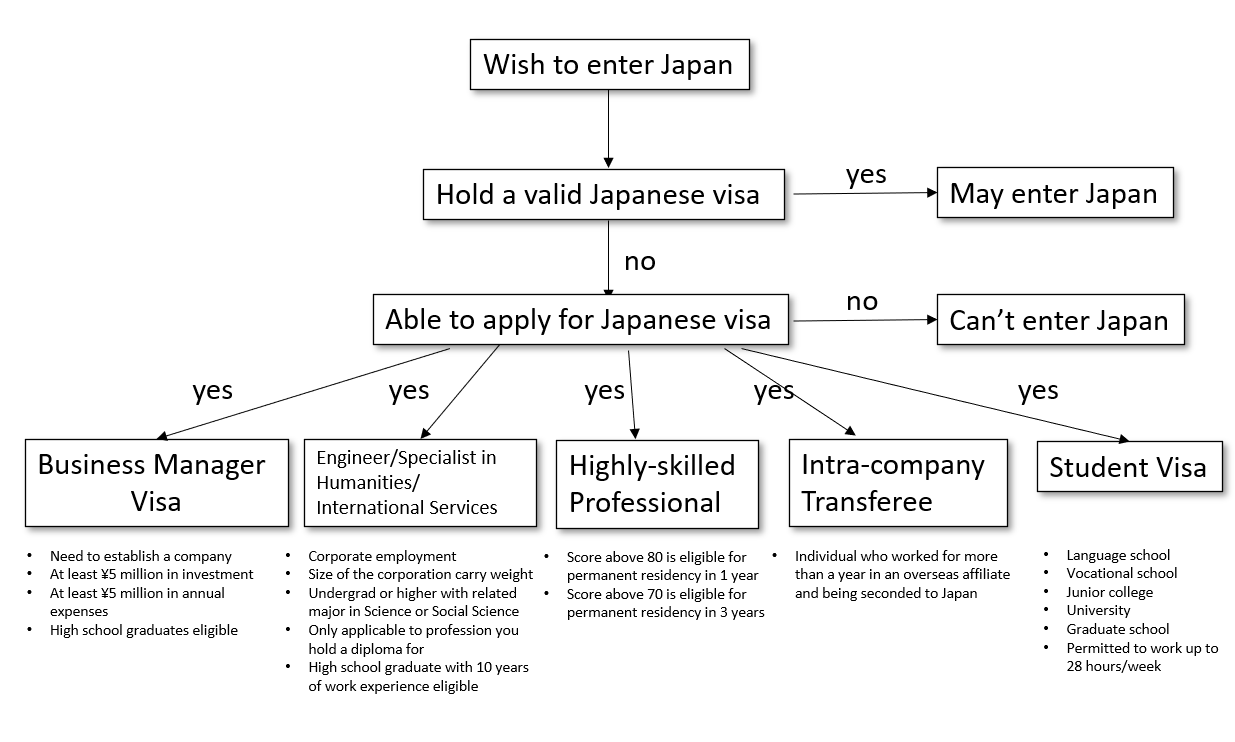
Short-term Stay Visa
Any foreign national wishing to enter Japan must have a valid passport, which, in principle, contain a visa corresponding
to his/her purpose of entry into Japan obtained in advance from a Japanese Embassy or Consulate.
When setting up an office, branch office or preparing to establish a corporation in Japan, first you must obtain a
temporary visitor’s visa at the Japanese Embassy/Consulate. Upon landing in Japan, the foreign national must then be
screened by, and receive a landing permission stamp from, an immigration office at the port of entry. (visa requirement
does not apply to entry by nationals of countries with which Japan has reciprocal visa exemption arrangement for
temporary visitor's visa)
Investment in Japan, market research and other preparatory activities for starting a business in Japan are generally
considered to be within the scope of short-term activities. The period of stay will be 90 days, 30 days, or 15 days.
Visa Types
| Business manager | Active in operating or managing international trade or other areas of business within a public or private organization in Japan. |
|---|---|
| Engineer Specialist in Humanities Internatioal Services | Engaged in services which require skills or knowledge pertinent to physical science, engineering or other natural science fields, or in services which require knowledge pertinentto jurisprudence, economics, sociology or other human science fields, or in services whichrequire special consideration or sensitivity based on experience with foreign culture, basedon a contract with a public or private organization in Japan. |
| Highly-skilled Professional | A points-based system based on “academic background,” “professional career,” “annual salary” and the like. If the total points reach a certain number (70 points), preferentialimmigration control and residency management treatment will be granted to the relevant person, with the aim of promoting the acceptance of highly-skilled foreign professionals in Japan. |
| Intra-company Transferee | A staff member transferred to a business office in Japan for a limited period of time from a business office established in a foreign country by a public or private organization which has its head office, branch office or other business office in Japan, to conduct work at said business office in Japan in regards to Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services. |
Acquisition of Visa
Necessary Documents for Visa Application
The following documentation is generally needed when applying for a working visa at a Japanese diplomatic mission
abroad after a Certificate of Eligibility has been issued:
Necessary Documents
- Visa application form
- Passport
- Certificate of Eligibility and copy thereof
- Full-face photograph (1-2 photos, 4.5 cm in height x 4.5 cm in width)
- Other documents that may be required for visa application process
FAQ about Visas
Are there any documents that need to be translated to Japanese during company establishment and visa
application?
All non-Japanese documents must all be translated to Japanese. We will provide you with the list of documents after a contract
has been signed with us, as we will know more in detail about your business.
Does a business manager visa have indefinite duration as long as there is reason for the
individual to stay and work?
Yes, but if the individual's duration of stay in Japan is too short, it may be deemed that the visa is not necessary for him/her and
the renewal may be denied. Also, it is very likely that you will not be granted a visa for more than one year.
Should an I stay in Japan for more than half a year even if I don’t have a reason to? Or, like business manager visa, as long as there is an acceptable reason to stay in Japan it is
indefinite?
Same as Q2. Business manager visa and engineer/specialist in humanities/international services visa are the
same. With a business manager visa, if your stay in Japan is short you many not be able to renew your visa.
Status of Residence
Foreign nationals entering and wish to reside in Japan must generally receive landing permission upon arrival at the airport, at
which point the residence status of the individual will be determined. The scope of activities in which a foreign individual may
engage during their stay in Japan is determined by their residence status.
Common Status of Residence in Japan
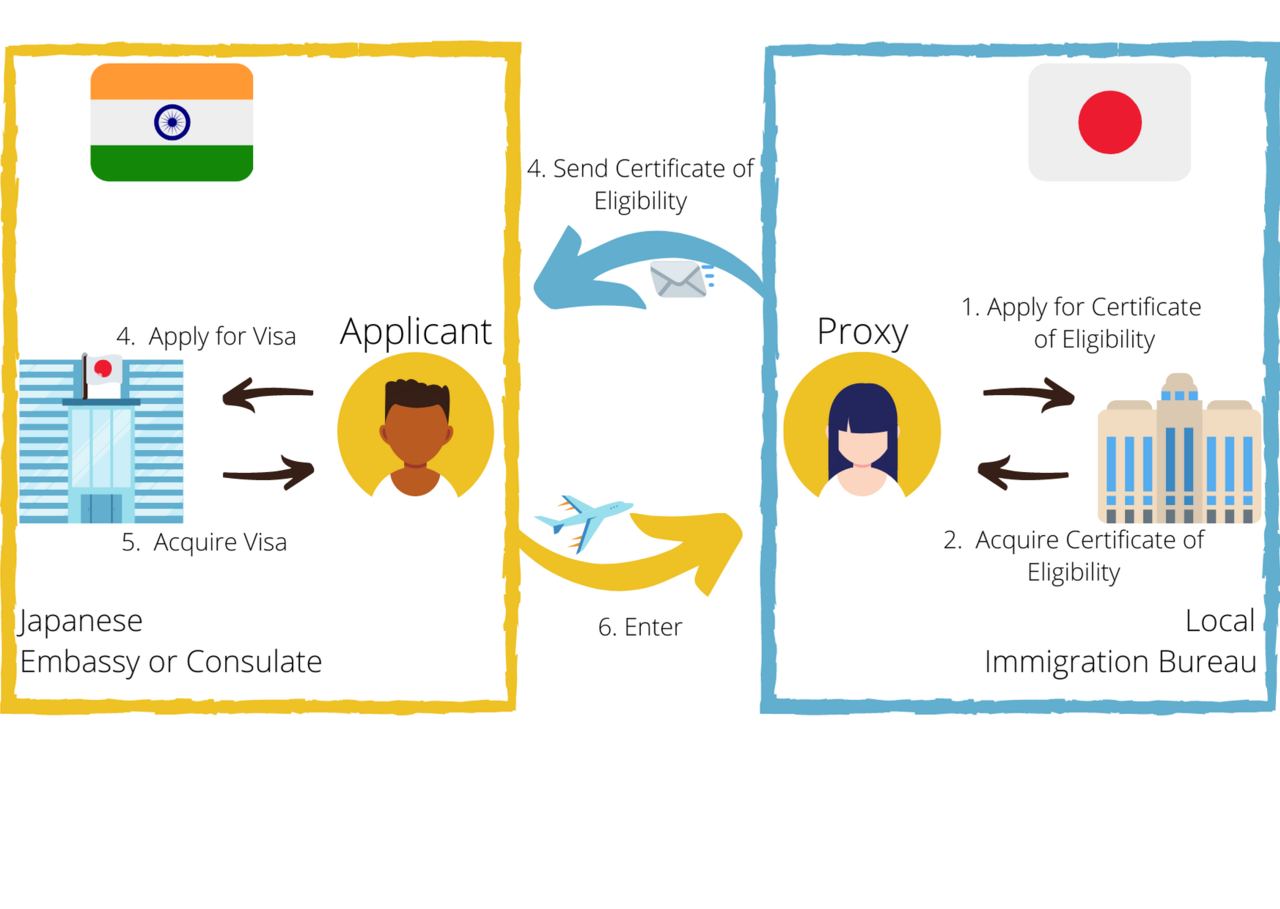
Process from acquisition of Certificate of Eligibility to acquisition of visa
<In Japan> Application for Certificate of Eligibility (submitted to Immigration Bureau in Japan) by the applicant or his/her proxy
<In Japan> Issue of Certificate of Eligibility (by Immigration Bureau in Japan); sent to applicant or his/her proxy in Japan
<Outside Japan> Visa application with Certificate of Eligibility at Japanese diplomatic mission abroad
<Outside Japan> Visa issuance at Japanese diplomatic mission abroad
<In Japan> Seal of landing verification, enter Japan
<In Japan> Residence card issued (applicable to major airports only)
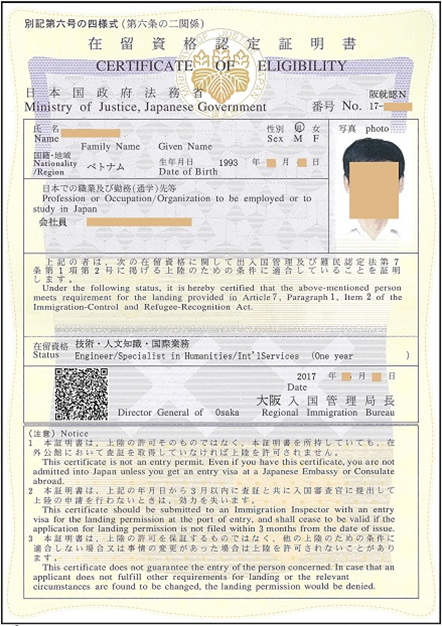
Documentation needed when applying for a Certificate of Eligibility
The Immigration Bureau in Japan often screens applications when a foreigner wishes to enter on a non “Temporary Visa” in
advance to determine whether or not the activities intended by the foreign national wishing to enter and reside in Japan
correspond to the conditions for the status of residence being sought; if it is determined that these activities do in fact meet the
conditions for the status of residence, a Certificate of Eligibility is issued.
<Required Documents> for New Establishment
- Application for Certificate of Eligibility
- One full-face photograph (4 cm in height x 3 cm in width)
- Return-mail envelope (with 392 yen postage affixed)
- A copy of employment agreement
- Certified copy of the company register of an organization of affiliation
- Company brochure, copy of financial statements of an
organization of affiliation in Japan - For new establishment; a business plan that clarifies
income and expenditure estimates
- If the organization is exempted from withholding at
source; certificate on the foreign corporation’s exemption from withholding at source or other document stating that the
organization does not require withholding at source. - If the organization is not exempted from withholding at
source; a copy of Notification on the Establishment of a Salary-Paying Office and a Statement of Collected Income Tax on
employment income and retirement income of the last three
months (a copy of the document with receipt date stamp) or if the organization is subject to special provisions regarding due dates, a document stating the approval for that is required.
Residence Card

A residence card is a card issued to foreign nationals residing legally in Japan
for the mid to long-term who have resident status under the Immigration
Control Act (“mid to long-term residents”) when they are granted a residence-
related permit, such as landing permission, permission for change of status of
residence, and permission for extension of period of stay. Mid to long-term
residents carry a resident card while living in Japan and are included in the
Basic Resident Register like Japanese nationals.
The card includes the following information: name, nationality/region, date of
birth, gender, status of residence, period of stay, and it includes information
such as work authorization and is required to be carried at all times.
In addition, foreign nationals to whom a resident card is issued are obliged to report their place of residence at the municipal office within 14 days of finding a residence
Corporate Taxes
National and Local Government
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, and under these prefectures, there are many more municipalities.
There are two types of taxes: those that are paid to the government and those that are paid to the prefectures and
municipalities listed above (these are called local governments).
Companies when being established may freely choose when their fiscal year starts. Most companies in Japan have a fiscal year that runs from April to March of the following year. Fiscal year from January to December of the following year is the
second most common option. For Joint-stock Company or LLC, the fiscal year is defined in the articles of incorporation.
Companies must calculate their income for each business year which is used to determine the corporate taxes to be levied on a corporate income. The amount of income used as the tax base for corporate taxes on income for each taxable year is determined by making the necessary tax adjustments to corporate profits calculated using accounting standards generally accepted as fair and appropriate.
Corporate Taxes
Consumption Tax

As described on the previous page,
the following taxes are levied on
"corporate income" which is
profit made through corporate
activities plus or minus the
necessary tax adjustments.
1.Corporate Tax(National Tax)
2.Corporate Inhabitant Tax(Local Tax)
3.Enterprise Tax(Local Tax)
4.Special Local Corporate Tax*
*National tax, although filings and payments are made to local governments
along with enterprise tax.
Corporate Tax Rate(SME)
Annual Taxable Income up to 8 million yen 15%
Annual Taxable Income over 8 million yen 23.4%
In addition, when corporate local tax, corporate enterprise tax and such
are also levied, the effective tax rates are approximately 25-35%.
The tax rates are subject to change.

The following domestic and import transactions, except for certain
transactions deemed non-taxable, are subject to consumption tax.
Consumption tax rate has been
raised to 10% from October 1, 2019.
A reduced tax rate of 8% will be applied to transactions
such as food and beverages that are deemed essential
Domestic transactions: the transfer or rental/lease
of assets or the provision of services as a business in
Japan by an enterprise for consideration.
Import transactions: foreign cargo retrieved from a
bonded zone
Individual Tax
Individual Income Tax
Salaries, wages, bonuses, and other similar compensation paid to residents in Japan are subject to tax withholding.
In addition, other prescribed income to residents such as interest, dividends, retirement allowance, compensation, fees, etc., to certain
professionals are subject to personal income tax.
Companies who pay income subject to withholding and must pay the taxation office the amount of tax withheld no later than the 10th
day of the month following that the income was paid.
A special measure is provided for small businesses with fewer than 10 employees on the payroll, which allows them to pay withholding
income tax in six-month installments twice a year (by July 10 and January 20).
Japan Market Entry FAQ
What is the difference between a registered seal (round seal), an unregistered seal (square seal) and a registered bank seal?
Do the names of investors have to appear on the bank book of the investment deposit?
Can I open a corporate bank account if the head office is a rental office?
When should I sign the contract for head office lease?
How is the business purpose of the company is determined?
If the type of business the company wishes to engage in required a permit from the government, is the Application for the permist also possible?
What if signature certificate is unattainable from my country?
Can the investment of LLC be made through an overseas bank account?
Can I get a copy of the real estate register?
Can a virtual office be used to set up a head office?
Can a corporate bank account be opened if the registerted head office is a virtual office?
Can I use my home address to register my company?
If there is more than one representative director, do they all need to be registered for their seals?
If I am a Japanese residing abroad, what do I need instead of a seal certificate?
Can more than one company be incorporated using the same address?
Is it possible to use online banking for the intial investment of the incorporation process?
Do I need approval from the Japanese government to establish a company from overseas?
Do Shareholders Have to Be Directors?
Is investment limited to cash?
Is it cheaper to set up a Joint-stock Company and a General Incorporated Association at the same time?
Does the signature certificate have a term of validity?
Why are companies like Apple and Amazon incorporated as an LLC?
Is it possible to set up a Joint-stock Company with a director who does not have a permanent address in Japan?
Why is it better to have a large amount of capital?
Can the capital be used before the company is established?
Which is the easiest form of corporation to remit profits to an overseas parent company?
Does the investors have unlimited liability in the event of a bankruptcy?
How much does it cost to increase capital after the establishment of the company?
How much does it cost to relocate the head office after the company is established?
Please fill out the required fields in the form below and click the submit button
Inquiries by email are available 24 hours a day.
Please note that it may take some time for us to reply to your inquiry.
If you do not receive a reply within 3 business days, please contact us again.
大見出し

ガルベラ・パートナーズは、税理士、社会保険労務士、司法書士、行政書士が1つの事務所に所属し、中小企業のサポートを得意とするワンストップ型コンサルティングファームです。
東京事務所
東京都港区虎ノ門3丁目23番6号
秀和虎ノ門三丁目ビル7階
日比谷線「神谷町駅」徒歩2分
大阪事務所
大阪市西区立売堀1丁目2番12号
本町平成ビル3階
四つ橋線「本町駅」徒歩2分
福岡事務所
博多区博多駅東1丁目5番8号
モアグランド博多ビル4階